Author : Saman Memarpour
January 2025
Petrochemical & Fertilizer Market Analysis
Market Overview
In January 2025, the petrochemical and fertilizer markets experienced dynamic shifts influenced by supply constraints, increasing demand in key agricultural regions, freight disruptions, and regulatory changes. The Middle East and Persian Gulf remained key export hubs, while India, Europe, and Latin America continued to drive demand.
Supply constraints were largely driven by
Iran's
gas
shortages, which restricted urea production and
delayed
Chinese
fertilizer
exports,
tightening
availability in global markets. The
Middle
East
played
a
crucial
role
in
filling
supply
gaps, but logistical challenges, including
freight
rate
surges
and
congestion
at
major
ports, impacted timely deliveries.
The demand surge from India and Latin America further fueled market volatility. India’s large fertilizer tenders increased procurement activity, influencing price hikes across Middle East and Baltic suppliers. Meanwhile, Europe's winter procurement cycle sustained higher import volumes, despite fluctuating ammonia prices due to oversupply and weak industrial demand.
Freight disruptions remained a major concern, with
shipping rates climbing due to limited vessel availability and rising fuel costs. Regulatory changes, including
sanctions affecting certain supply chains and China's uncertain export policies, added further instability to the market, creating pricing fluctuations across
key fertilizer categories.
January 2025 Petrochemical & Fertilizer Market Analysis
Key Developments in January 2025:
- India’s Fertilizer Demand Spike: Two major tenders were issued, increasing global demand for urea and NPK.
- Iran’s Gas Supply Constraints: Reduced availability led to lower urea production, impacting global supply chains.
- China’s Delayed Return to Exports: Uncertainty in Chinese exports created price speculation.
- Freight Rate Surge: Limited shipping capacity increased transport costs, affecting global pricing structures.
- Ammonia Market Weakness: Ammonia prices declined due to oversupply and weaker industrial demand.
- Geopolitical Factors: Trade restrictions and energy policies influenced market volatility.
Urea Market Trends
The global urea market showed strong resilience, with key buyers continuing to secure long-term supply contracts despite fluctuating supply dynamics. Market fundamentals remained bullish, driven by regional supply disruptions, strong tender activity, and competitive pricing strategies from key producers.
India’s procurement strategy was
crucial in sustaining high demand, with multiple tenders driving
Middle
Eastern
and
North
African
FOB
prices
upward. Additionally, supply chain limitations in
Iran,
Russia,
and
China created
temporary
supply
bottlenecks, prompting buyers to seek
alternative
sources
in
the
Baltic
region
and
North
America.
Global trade flows were also impacted by logistical issues, rising freight rates, and port congestion, which led to delayed shipments and tighter supply in certain markets. Some buyers opted for
long-term agreements to mitigate volatility risks, ensuring stability in their fertilizer procurement strategies.
The following table highlights
global urea price movements across key regions:
Global Urea Price Movements - January 2025, FOB (USD/Metric Tons)
| Region | Jan 2 | Jan 9 | Jan 16 | Jan 23 | Jan 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle East | 373 | 380 | 386 | 400 | 410 |
| Egypt | 415 | 430 | 432 | 435 | 445 |
| Baltic | 345 | 365 | 370 | 375 | 385 |
| US Gulf | 334 | 355 | 360 | 363 | 370 |
| Brazil CFR | 380 | 390 | 395 | 400 | 410 |
| India CFR | 369 | 369 | 410 | 415 | 425 |
Key Drivers Affecting Urea Prices
- Indian Tenders: Increased demand drove FOB Middle East prices to 410USDpmt.
- Iran’s Production Issues: Gas shortages constrained supply, keeping prices elevated.
- Europe & Brazil Procurement Increases: Stockpiling due to seasonal demand.
- China’s Uncertain Export Policy: Potential future market shifts if Chinese suppliers return.
- Natural Gas Price Fluctuations: Influencing urea production costs globally.
- Rising Freight Costs: Higher transportation expenses pushed FOB prices higher in key exporting hubs.
Chart: Urea Price Trends - January 2025 (USD/Metric Tons)

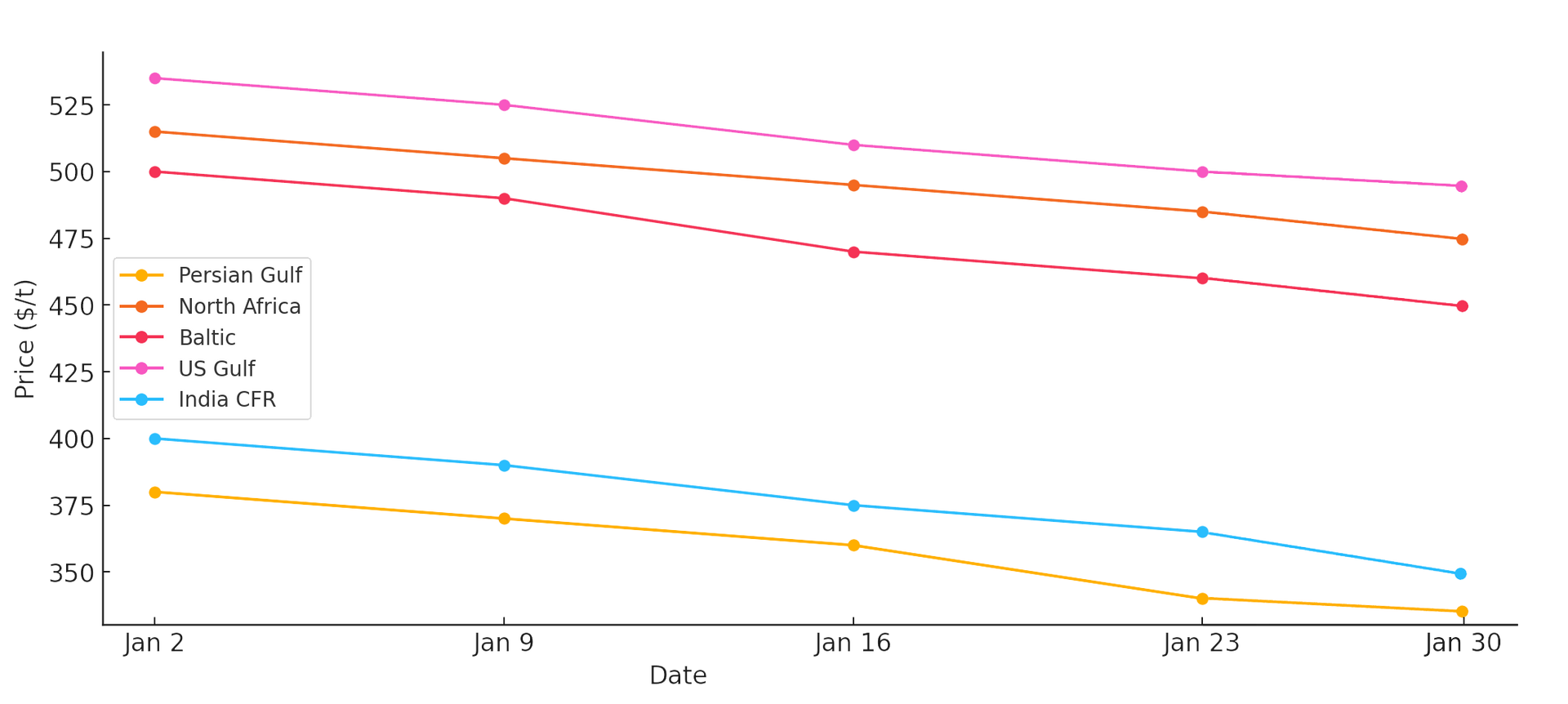
Ammonia Market Trends
Unlike urea, ammonia prices softened in January, reflecting a global surplus due to weaker demand from industrial consumers in Asia and Europe. The following table summarizes ammonia price movements for January 2025:
| Region | Jan 2 | Jan 9 | Jan 16 | Jan 23 | Jan 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persian Gulf | 380 | 370 | 360 | 340 | 330 |
| North Africa | 515 | 505 | 495 | 485 | 475 |
| Baltic | 500 | 490 | 470 | 460 | 450 |
| US Gulf | 535 | 525 | 510 | 500 | 490 |
| India CFR | 400 | 390 | 375 | 365 | 350 |
Ammonia Market Analysis
- Surplus Supply: Increased production in the Middle East and Indonesia pushed prices down.
- Industrial Demand Weakness: Slower economic growth in Asia and Europe reduced demand.
- Market Expectations: Traders anticipate further price corrections in Q1 2025.
- Freight Costs Impact: Shipping ammonia to India and Europe became more expensive, further squeezing margins.
Chart: Ammonia Price Trends - January 2025 (USD/Metric Tons)
Freight Market & Trade Flow Analysis
- Freight rates continued to rise across key fertilizer shipping routes due to limited vessel availability, increased fuel costs, and logistical constraints. A combination of high bunker fuel prices, port congestion, and surging demand for bulk carriers has exacerbated the cost increases.
- Shipping delays have been reported in major fertilizer export hubs such as the Persian Gulf, Baltic Sea, and China, leading to longer lead times for deliveries to key markets like India, Brazil, and Europe. Additionally, the shortage of available vessels for spot charters has further pressured freight rates, prompting many traders to secure long-term shipping contracts to mitigate risks.
- Market analysts expect freight costs to remain high through Q1 2025, particularly for routes involving long-haul shipments, as the global supply chain adjusts to logistical bottlenecks and fluctuating demand.
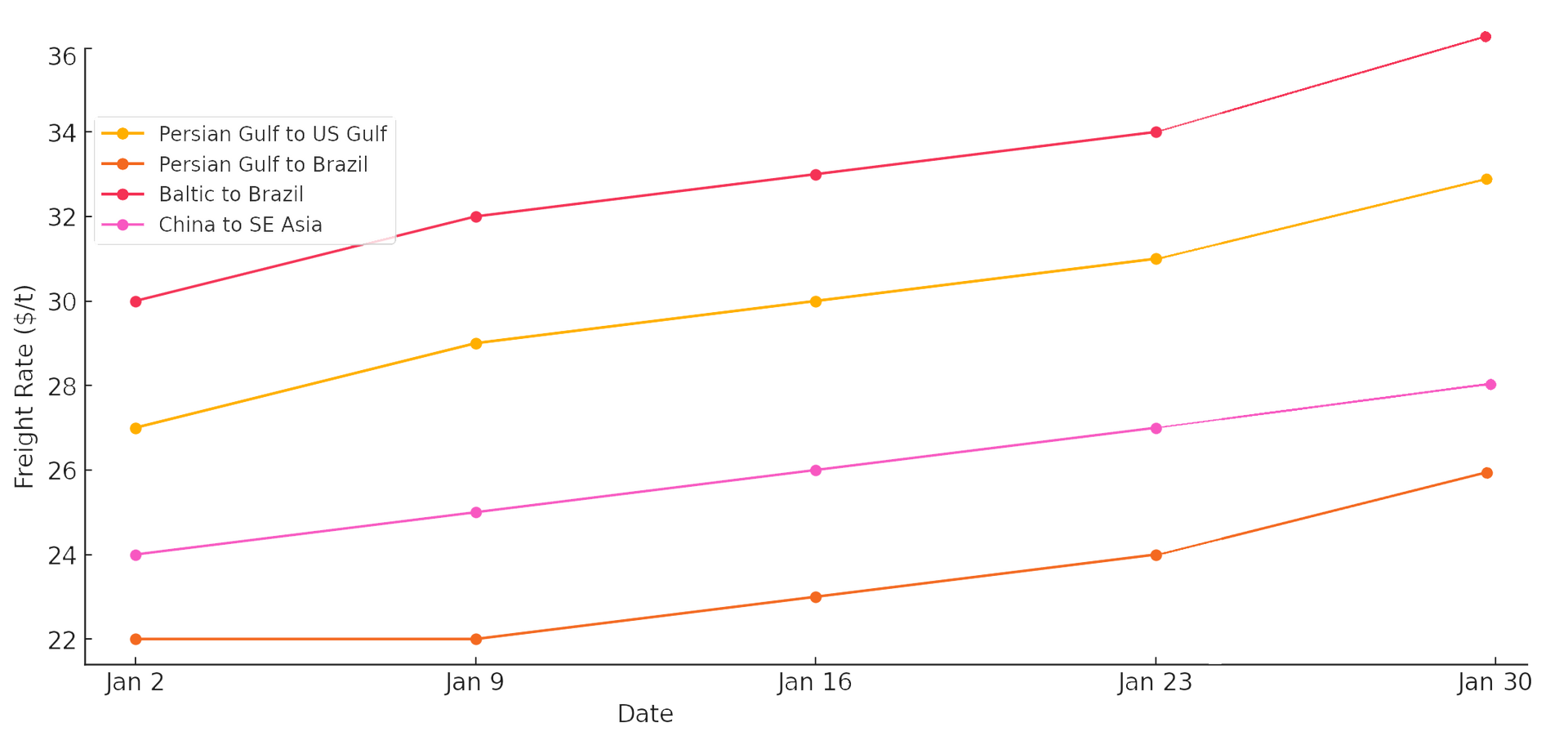
Freight Rates (USD/Metric Tons)
| Route | Jan 2 | Jan 9 | Jan 16 | Jan 23 | Jan 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persian Gulf to US Gulf | 27 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 33 |
| Persian Gulf to Brazil | 22 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 26 |
| Baltic to Brazil | 30 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 36 |
| China to SE Asia | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Freight Market Insights
- Increased Shipping Demand: Higher demand for long-haul shipments to Brazil and India.
- Rising Fuel Costs: Contributing to higher freight rates globally.
- Congestion in Major Ports: Delays in India and China affecting shipping schedules.
Chart: Freight Rate Trends - January 2025 (USD/Metric Tons)
Conclusion & Outlook
- Urea Prices: Likely to remain strong, supported by continued Indian tenders and limited Middle East supply. The Indian government’s procurement strategy has driven aggressive purchasing activity, further tightening global supply. Additionally, gas shortages in Iran and energy constraints in the Middle East continue to impact production levels, preventing a price decline. With European and Brazilian buyers increasing their pre-season stockpiling, the upward price trend is expected to hold, especially as freight costs rise and trade flows remain disrupted by shipping constraints. Meanwhile, China’s uncertain export policy keeps the market in suspense, with traders closely monitoring potential supply shifts in Q2 2025.
- Ammonia Prices: Expected to decline further due to persistent oversupply caused by increased production in the Middle East, North Africa, and Southeast Asia, as well as lower-than-expected demand from industrial and agricultural sectors. Weak economic growth in major ammonia-consuming regions such as Europe and China has led to reduced consumption, further pressuring prices downward. Additionally, high inventory levels in storage hubs and reduced purchasing activity from key importers like India and Brazil have contributed to the bearish market sentiment. Unless there is a significant disruption in supply chains or an unexpected demand rebound, ammonia prices are likely to continue their downward trajectory into Q1 2025.
- Freight Costs: High costs are expected to persist, especially for long-haul shipments due to several interrelated factors. The continued rise in bunker fuel prices, along with logistical bottlenecks at major export hubs, has exacerbated overall shipping expenses. Furthermore, port congestion in key fertilizer-exporting regions, including the Persian Gulf, China, and the Baltic Sea, has led to extended wait times and higher demurrage fees, further pressuring freight rates. Additionally, a shortage of available vessels—partly due to increased bulk carrier demand for other commodities—has forced traders to seek higher-cost shipping contracts. Given these constraints, analysts predict that freight costs will remain elevated through Q1 and Q2 2025, especially on routes servicing high-demand markets like India, Brazil, and West Africa.
- Potential Market Disruptions: Any policy changes in China or energy price shocks could shift pricing dynamics significantly. If China reopens fertilizer exports, it could lead to an influx of supply, putting downward pressure on global urea and ammonia prices. Conversely, if China maintains restrictions, the market may continue experiencing tight supply and elevated prices. Additionally, geopolitical events and energy crises, such as OPEC+ decisions on crude oil output or natural gas supply cuts from key exporters like Russia and the Middle East, could escalate production costs, further influencing market volatility. Traders and buyers will closely monitor these potential disruptions as they prepare for Q2 2025 market conditions.

